المياه الجوفية في قضاء المحمودية
وسبل استثمارها
رسالة تقدمت بها
سندس محمد علوان الزبيدي
إلى مجلس كلية التربية للبنات في جامعة بغدا
وهي جزء من متطلبات نيل شهادة الماجستير
في قسم الجغرافية
بإشراف
الأستاذ المساعد الدكتور
فخري خلف عبد الله البياتي
1432هـ - 2011م
الملخص
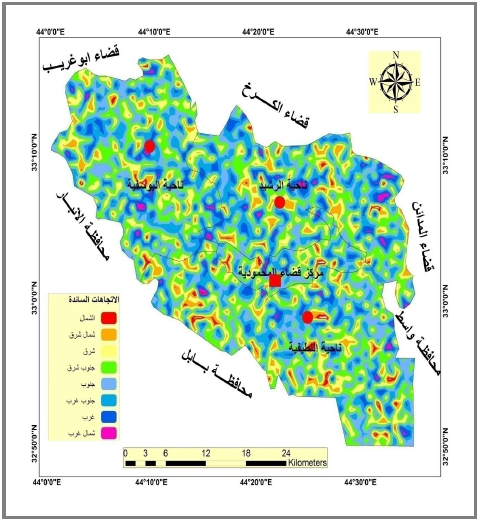
اسهمت دراسة المياه الجوفية في قضاء المحمودية في تعزيز دراسة الموارد المائية (الهيدروليكية)، والبالغ مساحته (1410.7) (كيلومتر مربع الواقع جنوب محافظة بغداد والمؤلف من أربعة نواحي هي (اليوسفية، والرشيد، ومركز المحمودية، واللطيفية( بوساطة التحليلات الكيميائية التي قيمت المياه الجوفية (كماً ونوعاً) ،وانجاز هذا العمل يتطلب عملاً مكتبياً وميدانياً ، ففي أثناء العمل الميداني تم جميع (16) عينة لمواقع مختارة للمنطقة على أساس طوبوغرافي تمثلت في مناطق أكتاف الأنهار ومنطقة السيل الفيضي ومنطقة - المنخفضات ضمن مدد زمنية مختلفة في أثناء مدة الزيادة والنقصان للسنة المائية (2010 - 2011)م، ومن أجل تحقيق هدف الدراسة في القاء الضوء على أهمية المياه الجوفية ولبيان مواصفاتها واحتمالية تلوثها في حالاتها الرهنة وتأثيرها في حاجات المنطقة وقد خلصت الدراسة إلى أن مساحة المنطقة تغطيها رسوبيات الزمن الرباعي والتي تعد أهم الخزانات الجوفية في المنطقة، إذ تشكل هذه الترسبات الخزان المائي المفتوح لعموم مساحة الحوض، وأن البنية الجيولوجية المنكشفة في الحوض تتدرج أعمارها بين المايوسين واليولوسين تغطيها رواسب الزمن الرباعي وبانحدار عام شمالي غربي جنوبي شرقي، مع انحدار طفيف - شمالي غربي جنوبي شرقي بمعدل (38) سم/كم وتقع المنطقة ضمن المناخ الصحراوي – الجاف.
توجد في منطقة الدراسة ثلاث وحدات تضاريسية تباينت من حيث ارتفاعها عن مستوى سطح البحر، تشكلت الأولى نتيجة عمليات الإرساب حول أكتاف الأنهار ( دجلة والفرات) والمنطقة الثانية السهل الفيضي لعموم المنطقة والثالثة بالمنخفضات التي كونت السبخات المالحة خاصة في وسط المنطقة وجنوبها الغربي.
أظهرت الدراسة الرسوبية والتحليل الحجمي للرسوبيات في منطقة الدراسة بأنها تتكون بصورة رئيسة من الغرين الطيني وتتراوح نسبة الغرين مابين 24 - 66 %، أما الطين فيأتي في المرتبة الثانية وتتراوح بين 21 - 50 %، بينما الرمل تكون نسبته مابين 4 - 21%.
ويتميز النبات الطبيعي بانتشاره بين المساحات المزروعة وبالقرب من مشاريع الري والبزل التي تنتشر فيها نباتات مائية ونباتات معمرة كالقصب والصفصاف، وتنتشر شبكة من المبازل تنخفض فيها المناسيب عن مستوى سطح البحر أو مستوى دجلة والفرات لتخليص المنطقة من مشكلة الملوحة التي تعاني منها المساحات الزراعية لتصب في المصب العام والتي لها دور في استصلاح الرقعة الزراعية.
أظهرت نتائج التحليلات الهيدروكيميائية التي إجريت على النماذج المائية في فصل الصيف والشتاء، أن المياه الجوفية لمنطقة الدراسة عديمة اللون والرائحة باستثناء بئر رقم) (86.81) حيث كان لونه أصفر مخضر لاحتوائه على المواد العضوية ، وتميزت المياه كذلك بارتفاع العكورة (Turbidity) في ثلاثة مواقع (80 - 83 - 86) أعلى من الحدود المسموحة بها وارتفاع واضح في قيم الكبريتات والكلورايد يمكن أن يعزى إلى وجود أملاح المتبخرات مثل الجبس والهلايت إذ تعد المصدر الأساسي لتلك الأيونات الرئيسة والملوحة بصورة عامة في المياه الجوفية. بوساطة نتائج التحليلات للعناصر النادرة وجد أن قيم الرصاص والكادميوم والخارصين والبورون زيادة واضحة بينما الحديد والمنغنيز والنحاس والنترات ضمن الحدود المسموح بها. وجد أن المياه الجوفية غير صالحة للشرب وإنها يمكن استعمالها في ري أغلب المحاصيل الزراعية ولكن استعمالها يكون محدوداً وأغلبها محاصيل تتحمل الملوحة مثل الجت والبرسيم، ويكون استعمالها محدوداً في الصناعة وهي غير صالحة للاستعمال في الشرب للحيوانات خاصة الدواجن.
ويواجه الاستعمال الزراعي في المنطقة مشاكل عدة أهمها تلوث المياه الجوفية نتيجة القاء المياه العادمة وغيرها إلى المسطحات المائية التي تغذي الخزان الجوفي علاوة على الاستخدام الخاطئ للمزراعين بالاعتماد على المبازل لسقي المزروعات والتي تدخل أيضاً إلى المياه الجوفية بما تحلمه من أسمدة ومبيدات متنوعة، واحتمالية نفاذية مياه الآبار نتيجة الضخ الجائر للاهالي وتردي نوعيتها لارتفاع نسبة الأملاح وبعض العناصر النادرة الناتجة عن سوء استعمال الآبار وعدم وجود غطاء محكم في أغلب الأحيان وقد تم تعيين المناطق الخالية من التلوث في منطقة الدراسة تقدر ب (157.808) دونم وهي مساحة لابأس بها في الاستثمار الزراعي وبمساحة (28200) دونم تكون ملوحتها ما بين (790 - 2400) ممغم/لتر - وهي أقل نسبة في المنطقة، إذ أن الملوحة المدروسة في الحوض تمثلت بتغايرها الموقعي ومع المساحة إذ تقل ملوحة المياه الجوفية بالقرب من المصادر المائية السطحية لنهري دجلة والفرات المشاريع المائية من قناة الفلوجة الموحدة.
- وفي الختام آمل أن يكون هذا الجهد المتواضع قد حقق بعض الاسهامات في دراسة الموراد المائية (المياه الجوفية) لما لها من علاقة وخطط التنمية في البلد.
The Ground Water in Al- Mahmoodia Area and the ways of its Investment
A thesis submitted to the council of the college Education for women in partial fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of master in the department of Geography
By
Sundus MohammedAlwan Alzubaidy
Supervised by
Dr.
Fakhri Khalaf Abdullah Al Bayaty
2011 - 1432
Abstract
The ground water has contributed to reinforce the study of the Geography of the water resouras (Hydrologia) in Al- Mahmoodia area by the range (1410.7)km2 in the south of Baghdad which composed of Al- Rasheed , Al- Mahmoodia center, Al- Usifia and Al- Latifia.
The achievement of the study requires library and field work. In the field work, sixteen samples have been taken to the chosen areas and it is based on Topographic hase represented in the regions of the (River leav), (Basin) and the area of the (depression) within different period, of time . In other words, through the time of increament and decrease for the water year (2010- 2011).
To achieve the aim of the study , it should shed light on the significance of the underground water, show it's features and the probability of its pollution in it's current cases and it's effect on the requirement of the area. The study summarizes the work by showing that the range of the area is covered by the sediments of the (quarternary) which are considered as one of the important underground fountains in the region. It shows that these sediments form the water store which is peon to the most area. The age of the uncover geological structure in the area is between the (Mayoseen) and (Haloseen) and is covered by the sediments of the quarternary with general fall North west- South east, and light fall North- South with average (38) cm/km. The area lies within the dried desert climate. There are three reliefunits in the area of the study .
They are different according to it's height from the level of round the rivers (Tigris and Euphrates). The second is the (River leav) for the most area. Finally is the (depression) which form the saltymoor especially in the middle of the area and it's East south .
The study of the sediments and size analysis of it in the area of the study reveals that it is basically composed of (clay loam) and its average is between (24-66)% While the clay is in the second level between (21-50)%, and finally the sand between(4- 21)%.
The natural planet in the area is characterized by its growth between the farms and near the watering and puncturing projects in which spread the watering planets and perennial like the canes , and the willow . In addition to that there is anet of puncturing spread with the decrease of the averages about the level of the sea or the level of Tigris and Euphrates to make the area away of the problems of salt which the farms suffer, to flow in the general month of the river which has the role to reclaim the planting area or reqion.
It is concluded from the hydrocemical analysis done on the watering samples in summer and winter that the ground water of the studying sample is colorless and without smell except the wall numbered (81.86) where it's color is greeny yellow because it consists of organic materials. The water is also characterized by its high turbidity to reach more than the limits allowed in three areas (80, 83, 86). Besides, the is a clear increase in the sulfate and chlorine which are due to the existence of the vapors salt like plaster and Helight which are considered the main source to the basic ions and the salt in general in the ground water . It is found through the results of the analysis of the rare elements lik lead , Cadmium, Zinc and Boron are in clear increase while Iron, Manganese , Brass and Nitrate are within the allowed limits. Thus, it is concluded that the ground water is undrinkable and can be used within alimit to water most of planks and basically those which stand the salt like the vegetable plant (Jet and Berseem) while in the industry and manufacture, it is limitly used and is undrinkable to animals especially the domestic.
According to the planting investment, it faces many problems in the areas like the pollution of the ground water by throwing rabish water and other unuseful thing in the water flats that feed the ground stores, besides the mistakes the farmer do by depending on the puncturing to water the vegetables which also go to the ground water with what it carry as compost and different kinds of insecticide , and the probability of the dry of the walls as a source for people and the bad kinds of it because of the increase of the salt and some rare elements resulted by the misuse of the wall, besides the covers which are not well used in most of the times.
Through the study and in the sample , it is found that there are certain areas which are devoid of pollution . It is about (157.808) acres. It is well for planding usage with range (28200) acres with salt between (790 -2400)mlg/Land it is the less average in the sample where the salt is represend by it's place difference in the Basin. The study also shows that the salt of the ground water is less near the water projects from the united channel of Al- Faluja.
Eventually, it is hoped that this effort has achieved some of the works in the study of the water source ground water because of it's relations and plans to promote the country.
تحميل الرسالة
لا تنسى انك حملت الرسالة من موقع كوكب المنى








0 تعليقات
شكرا لتعليقك .. سيتم الرد عليكم في اقرب وقت ممكن .
كوكب المنى